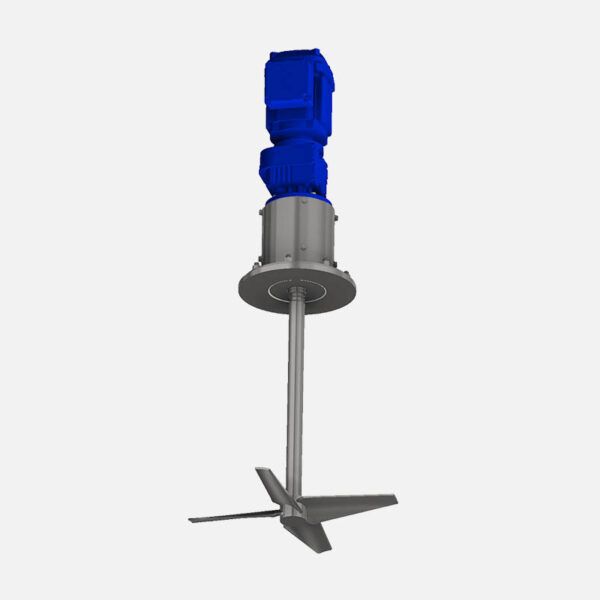

Agitator for Water Treatment Plant
Agitator for Water Treatment Plant: An Essential Component for Effective Water Purification
In modern water treatment facilities, the agitator for water treatment plant plays a critical role in ensuring the effective purification of water. Whether the plant is municipal or industrial, proper mixing is crucial for a wide range of treatment processes, including coagulation and flocculation, chemical dosing, and suspension mixing. This article delves deep into how different types of industrial, such as paddle, propeller mixers, and mechanical Paddle contribute to high-efficiency water treatment systems.

What is an Agitator for Water Treatment Plant?
An for water treatment plant is a mechanical device used to stir, mix, or circulate fluids in tanks and basins. These Stirrer ensure uniform distribution of chemicals, solids, and other additives, optimizing reactions and settling processes. From enhancing water mixing to ensuring even chemical dosing, these devices are indispensable for achieving regulatory water quality standards.
Read also:
Stirrer
Industrial Agitator
Water Agitator Mixing: The Foundation of Water Treatment
Water mixing is the fundamental action performed by an Mixer. In a water treatment plant, whether for drinking or industrial reuse, achieving homogeneity in the water is vital. Proper water mixing ensures that any introduced chemicals or particles are evenly distributed. Uneven mixing can result in poor treatment efficiency, wastage of chemicals, and non-compliance with water quality standards.
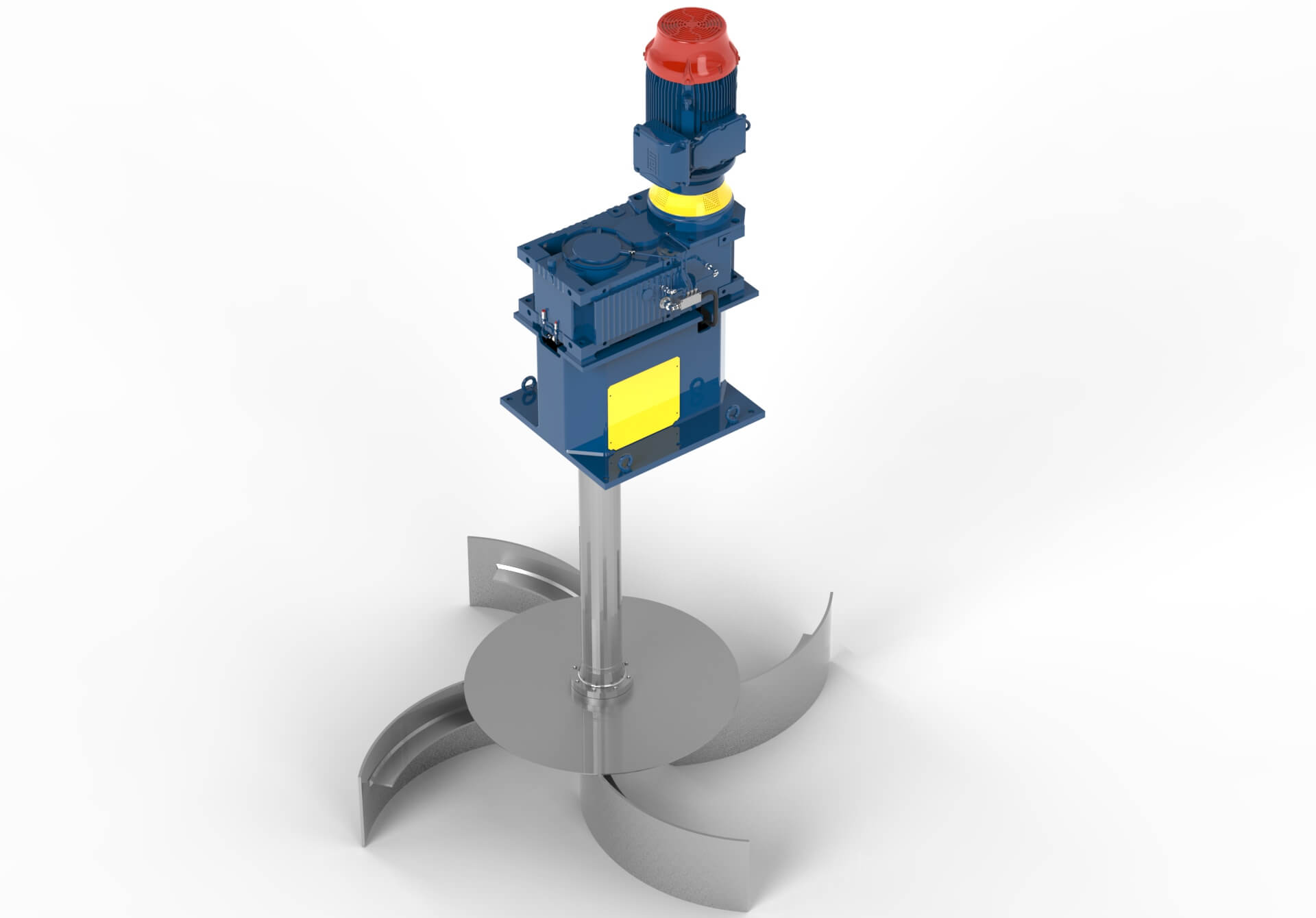 adjustable speed and torque are ideal for variable mixing needs, whether it's for high-intensity mixing during coagulation and flocculation or gentle stirring during sedimentation.
adjustable speed and torque are ideal for variable mixing needs, whether it's for high-intensity mixing during coagulation and flocculation or gentle stirring during sedimentation.Coagulation and Flocculation: Aided by Efficient Agitation
Coagulation and flocculation are two crucial stages in water treatment that require controlled and uniform mixing. During coagulation, chemical coagulants like alum are added to destabilize particles.mix these chemicals quickly to distribute them throughout the water. In the flocculation stage, gentle agitation encourages the formation of larger flocs that can be easily removed through sedimentation or filtration.
A high-performance mechanical ensures that the mixing intensity decreases progressively, facilitating optimal floc formation without breaking them apart. In this context, paddle and propeller mixers are commonly used due to their ability to provide slow, uniform mixing that promotes floc growth.
Chemical Dosing: Accurate Mixing for Desired Results
Precise chemical dosing is vital for water treatment success. An for water treatment ensures that dosed chemicals, whether coagulants, disinfectants, or pH adjusters, are instantly and evenly mixed with the incoming water stream. Inaccurate mixing can lead to chemical hotspots or under-treatment, both of which compromise water quality.
used in chemical dosing systems are usually designed for high turbulence mixing, depending on the reaction time and chemical type. These are often paired with automated dosing systems to ensure synchronized operations.
Suspension Mixing: Keeping Solids in Motion
Suspension mixing refers to keeping insoluble particles uniformly suspended in water to prevent settling during treatment. This is particularly important when dealing with sludge, lime, or other solid chemical additives. A robust industrial is designed to maintain suspension without excessive energy consumption.
Mechanical equipped with specially designed impellers or paddles help in achieving consistent suspension mixing. This not only ensures uniform treatment but also extends the life of downstream filtration and membrane systems by preventing clogging due to sedimentation.
Types of Industrial for Water Treatment
There are several types of industrial used in water treatment plants, each serving a specific purpose depending on the process requirements.
1. Mechanical
A mechanical is one of the most common types used. It operates using a motor-driven shaft and impeller to mix water and chemicals. These are reliable and suitable for both high-shear and low-shear applications, from coagulation and flocculation to chemical dosing.
2. Paddle
A paddle Stirrer consists of flat blades mounted on a rotating shaft. It's ideal for gentle mixing and is widely used during the flocculation stage. Paddle mixer maintain slow and uniform agitation, helping in the growth of flocs without breaking them apart.
3. Propeller Mixer
A propeller mixer is a high-speed, high-efficiency mixer. It is especially effective in processes that require fast mixing such as chemical dosing and initial coagulation. These mixers are compact and can be easily integrated into vertical or horizontal tanks.
Choosing the Right Mixer for Water Treatment
When selecting a mixer for water treatment, various factors must be considered:
-
Tank size and shape
-
Viscosity of the fluids
-
Chemical properties
-
Required flow pattern
-
Stage of treatment (coagulation, flocculation, etc.)
An ideal Stirrer for water treatment will offer flexibility in speed, power, and impeller type to cater to these varying needs. Advanced systems even come with programmable logic controls (PLCs) for smart, automated operation.
Energy Efficiency and Maintenance
Modern industrial Stirrer are designed with energy efficiency in mind. Variable frequency drives (VFDs) help optimize power consumption by adjusting the mixing speed based on real-time process requirements. Additionally, innovations in bearing and seal technology reduce maintenance frequency and operational downtime.
Proper maintenance is key to ensuring longevity and performance. Routine inspection of blades, shafts, and seals, along with timely lubrication, can prevent unexpected failures.
FAQs- Agitator
1. What is the purpose of an mixer in a water treatment plant?
An mixer for water treatment ensures proper mixing of chemicals, suspensions, and water to facilitate processes like coagulation, flocculation, and chemical dosing for effective water purification.
2. Which type of mixer is best for flocculation?
A paddle mixer is best for flocculation as it provides gentle, uniform mixing that helps in forming large, settleable flocs without breaking them.
3. How does a propeller mixer differ from a paddle Mixer?
A propeller mixer operates at higher speeds and is suited for rapid mixing, while a paddle Mixer provides slower, controlled agitation ideal for delicate processes like flocculation.
Our Blogs
- IoT Based Industrial Automation for Pump & Other Applications
- Dosing Pump Spares
- Dosing Pump Repair Service
- Agitator for Water Treatment Plant
- Stirrer: The Ultimate Mixing Tool
- Industrial Agitator: Mixer, Design, Machine, Manufacturer
- Image: Dosing Done Right - Customized Dosing Solutions for Precision Control
- High-Performance Motor Driven Systems for Diverse Applications
- Unlocking the Power of Chemical Dosing in Composite Manufacturing
- High-Efficiency Hydraulic Dosing Pumps for Seamless Fluid Control
- Dosing Skids - Streamlining Chemical Dosing Operations
- Monoblock Pumps - Reliable and Efficient Fluid Handling Solutions
- Dosing Skids - Streamlining Chemical Dosing Operations
- IBC Stirrer - Efficient Mixing for Intermediate Bulk Containers
- IBC Agitator - Efficient Mixing for Intermediate Bulk Containers
- Chemical Dosing Skid - Streamlining Your Chemical Dosing Operations
- Actuated Dosing Pumps - Precision and Reliability
- Mechanical Dosing Pump - Precision and Reliability
- Automating Precision: Exploring Automatic Chemical Dosing Systems
- Precision Dosing with Our Mechanical Actuated Dosing Pumps
- Mastering Mixing: Introducing Our Powerful Disperser Agitator
- Customized Dosing Solutions: Tailored Precision for Your Needs
- Electric Dosing Pump
- Customized Dosing Manufacturer: Tailored Solutions for Precision Dosing
- Flash Mixer: The Versatile Solution for Rapid Mixing
- Precision Pumping with Sarayu Engineering's Motor Driven Diaphragm Pumps
- Precision Dosing, Simplified: The Benefits of Chemical Dosing Skids
- Keeping it Moving: Unveiling the Power of IBC Agitators for Efficient Mixing
- Guardians Against Flames: A Comprehensive Guide to Fire Fighting Pumps
- Powering Up with Air: Exploring the Advantages of Pneumatic Agitators
- Keeping it Stirred: Unveiling the Power of Industrial Agitators in Mixing Applications
- The Heart of Reliable Dosing: Exploring the Advantages of Diaphragm Pumps
- Mastering Metering: Unveiling the Advantages of Dosing Skids for Precise Chemical Injection
- 2024 Guide to Dosing Pumps: Precision in Fluid Management
- The Versatility of Monoblock Pumps
- The Advantages of Automatic Water Dosing Systems
- The Importance of Flocculators in Water Treatment
- The Role of Industrial Agitators in Mixing Applications
- Demystifying Hydraulic Dosing Pumps: A Comprehensive Guide
- Unlocking Efficiency: The Role of Industrial Pumps in Streamlining Operations
- Chemical Pumps manufacturer in Gujarat
- Stirrer manufacturer in Gujarat
- Industrial Agitator manufacturer in Gujarat
- Industrial Centrifugal Pumps manufacturer in Gujarat
- Industrial Centrifugal Pumps supplier in Gujarat
- AODD Pumps manufacturer in Gujarat
- AODD Pumps supplier in Gujarat
- RO Skid manufacturer in Gujarat
- RO Skid supplier in Gujarat
- Dosing Systems manufacturer in Gujarat
- Dosing Systems supplier in Gujarat
- Chemical Dosing Pumps manufacturer in Gujarat
- Chemical Dosing Pumps supplier in Gujarat
- Mechanical Dosing Pumps manufacturer in Gujarat
- Mechanical Dosing Pumps supplier in Gujarat
- Hydraulic Dosing Pumps manufacturer in Gujarat
- Hydraulic Dosing Pumps supplier in Gujarat
- Electronic Dosing Pumps manufacturer in Gujarat
- Chemical Pumps manufacturer in india
- Stirrer manufacturer in india
- Electronic Dosing Pumps supplier in Gujarat
- Industrial Agitator manufacturer in india
- Mechanical Dosing Pumps manufacturer in India
- Industrial Centrifugal Pumps manufacturer in India
- Industrial Centrifugal Pumps supplier in India
- AODD Pumps manufacturer in India
- AODD Pumps supplier in India
- RO Skid manufacturer
- RO Skid supplier
- Dosing Systems manufacturer in India
- Dosing Systems supplier in India
- Chemical Dosing Pumps manufacturer in India
- Chemical Dosing Pumps supplier in India
- Mechanical Dosing Pumps supplier in India
- Hydraulic Dosing Pumps manufacturer in India
- Hydraulic Dosing Pumps supplier in India
- Electronic Dosing Pumps manufacturer in India
- Electronic Dosing Pumps supplier in India
